China’s Population Crossroads: A Look At Trends And Projections For 2025
China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025
Related Articles: China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025
- 3.1 Understanding the Shift: Key Drivers of Change
- 3.2 China’s Population Trends by 2025: Projections and Implications
- 3.3 China’s Population Trends and the Future
- 3.4 China’s Population Trends and Global Implications
- 3.5 Related Searches
- 3.6 FAQs
- 3.7 Tips
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025

China’s population trends are undergoing a profound transformation, with significant implications for the country’s economic, social, and political landscape. As the world’s most populous nation, China’s demographic trajectory is closely watched and analyzed. This article will delve into the key population trends expected by 2025, examining the driving forces behind these changes and their potential impact.
Understanding the Shift: Key Drivers of Change
China’s population trends are driven by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Declining Fertility Rate: The country’s total fertility rate (TFR) has been steadily declining for decades, falling below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman. In 2022, the TFR stood at 1.15, indicating a significant shortfall in births needed to sustain the population. This decline is attributed to various factors, including economic pressures, rising living costs, urbanization, and changing social norms.
- Aging Population: The combination of declining birth rates and increasing life expectancy has led to a rapidly aging population. By 2025, China is projected to have over 250 million individuals aged 65 and older, representing a significant strain on social security systems and healthcare infrastructure.
- One-Child Policy: While officially abolished in 2016, the decades-long one-child policy continues to have a lasting impact on China’s demographics. The policy resulted in a significant reduction in births, creating a demographic imbalance that is now being felt through a shrinking workforce and an aging population.
- Urbanization: China’s rapid urbanization has contributed to a decline in rural populations as individuals migrate to cities in search of better economic opportunities. This migration has also impacted fertility rates, as urban lifestyles often lead to smaller families.
China’s Population Trends by 2025: Projections and Implications
China’s population trends are expected to continue along their current path, leading to several key projections for 2025:
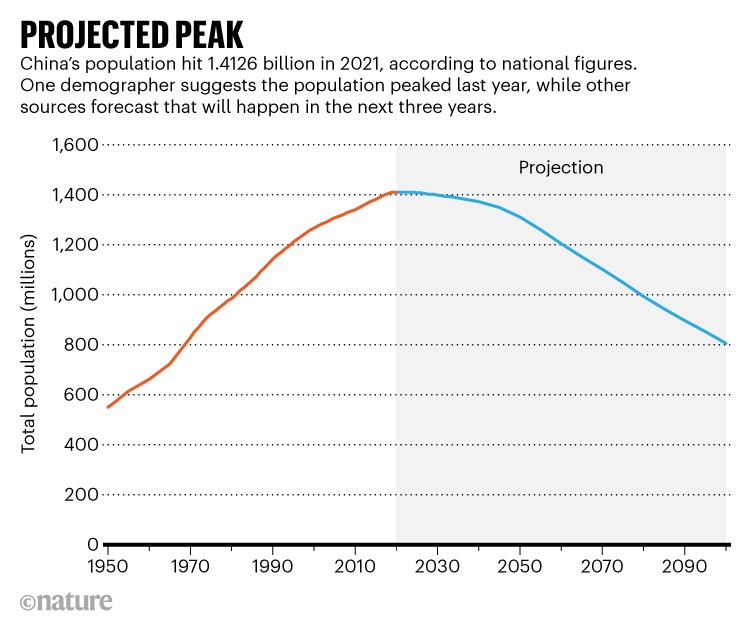
- Population Peak: China’s population is projected to peak around 2025, reaching approximately 1.45 billion. This peak will mark the beginning of a long-term decline in population size.
- Shrinking Workforce: As the population ages and birth rates remain low, China’s workforce is expected to shrink. This will have significant implications for economic growth, as the country faces a potential labor shortage.
- Increased Dependency Ratio: The aging population will lead to a higher dependency ratio, meaning there will be fewer working-age individuals supporting a larger number of retirees. This will place a strain on social security systems and healthcare infrastructure.
- Economic Impact: The shrinking workforce and aging population will have a significant impact on China’s economic growth. While China has a large savings pool and a robust manufacturing sector, the potential labor shortage could hamper future economic development.
China’s Population Trends and the Future
The demographic shifts currently underway in China present both challenges and opportunities. The country faces a need to adapt its policies and strategies to address the challenges posed by an aging population and shrinking workforce.
Key areas of focus include:
- Enhancing Labor Productivity: Investing in education, training, and technological advancements to improve labor productivity and mitigate the impact of a shrinking workforce.
- Strengthening Social Security Systems: Ensuring adequate financial support for an aging population through robust pension systems and healthcare programs.
- Promoting Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship to drive economic growth and create new employment opportunities.
- Managing Urbanization: Addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization, such as housing affordability, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability.
China’s Population Trends and Global Implications
China’s demographic transition has global implications, impacting international trade, investment, and geopolitical dynamics.
- Global Economic Impact: China’s declining workforce could affect global supply chains and potentially lead to higher prices for goods and services.
- Geopolitical Shifts: The changing demographics in China could influence the country’s foreign policy and its role in global affairs.
- Global Aging: China’s aging population is a trend mirrored by many other countries, highlighting the need for global solutions to address the challenges of an aging world.
Related Searches
1. China’s One-Child Policy:
The one-child policy, implemented in 1979 and abolished in 2016, had a profound impact on China’s population structure. It resulted in a significant reduction in birth rates, contributing to the current demographic imbalance. The policy’s unintended consequences, such as a skewed sex ratio and a shrinking workforce, continue to be felt today.
2. China’s Aging Population:
China’s aging population is a significant demographic challenge. By 2025, the number of individuals aged 65 and older is projected to exceed 250 million. This aging population will place a strain on social security systems, healthcare infrastructure, and the economy.
3. China’s Birth Rate:
China’s total fertility rate (TFR) has been steadily declining for decades, falling below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman. In 2022, the TFR stood at 1.15, indicating a significant shortfall in births needed to sustain the population. The decline in birth rates is attributed to various factors, including economic pressures, rising living costs, urbanization, and changing social norms.
4. China’s Urbanization:
China’s rapid urbanization has contributed to a decline in rural populations as individuals migrate to cities in search of better economic opportunities. This migration has also impacted fertility rates, as urban lifestyles often lead to smaller families. Urbanization has also presented challenges, such as housing affordability, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability.
5. China’s Economic Growth:
The shrinking workforce and aging population will have a significant impact on China’s economic growth. While China has a large savings pool and a robust manufacturing sector, the potential labor shortage could hamper future economic development.
6. China’s Social Security System:
China’s social security system is facing increasing pressure due to the aging population. The system is designed to provide financial support for retirees, but the shrinking workforce and rising healthcare costs are putting a strain on its sustainability.
7. China’s Healthcare System:
The aging population is placing a significant strain on China’s healthcare system. The demand for healthcare services is increasing, while the supply of healthcare professionals is not keeping pace.
8. China’s Foreign Policy:
China’s demographic changes are likely to influence its foreign policy. The country’s focus on economic development and its desire to secure access to resources could lead to increased international engagement.
FAQs
1. What is China’s current population?
China’s current population is approximately 1.45 billion, making it the world’s most populous nation.
2. When is China’s population expected to peak?
China’s population is projected to peak around 2025, reaching approximately 1.45 billion.
3. What is the impact of China’s aging population on the economy?
China’s aging population will lead to a shrinking workforce and a higher dependency ratio, placing a strain on economic growth and social security systems.
4. What measures is China taking to address its demographic challenges?
China is implementing various policies to address its demographic challenges, including promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, investing in education and training, strengthening social security systems, and managing urbanization.
5. How will China’s population trends impact global affairs?
China’s demographic changes will have implications for global trade, investment, and geopolitical dynamics. The country’s declining workforce could affect global supply chains, while its aging population could lead to increased international engagement.
Tips
- Stay informed: Keep up with the latest demographic trends and projections for China.
- Understand the implications: Consider how China’s population trends will impact businesses, investments, and global affairs.
- Adapt strategies: Adjust business strategies and investment decisions to account for the changing demographic landscape in China.
- Invest in education and training: Support initiatives that promote education and skills development to address the potential labor shortage.
- Promote innovation and entrepreneurship: Encourage innovation and entrepreneurship to create new economic opportunities and jobs.
Conclusion
China’s population trends are undergoing a profound transformation, with far-reaching implications for the country and the world. The declining fertility rate, aging population, and shrinking workforce present significant challenges, but also opportunities for innovation and adaptation. By understanding the drivers of these trends and their potential impact, individuals, businesses, and governments can make informed decisions and prepare for the future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into China’s Population Crossroads: A Look at Trends and Projections for 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!