Navigating The Future Of Food: Trends Shaping The Industry In 2025
Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
Related Articles: Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Plant-Based Foods
- 3.2 2. Personalized Nutrition and Dietary Needs
- 3.3 3. Food Waste Reduction and Sustainability
- 3.4 4. Food Delivery and Convenience
- 3.5 5. The Rise of the "Conscious Consumer"
- 3.6 6. Food Technology and Innovation
- 3.7 7. Food Safety and Traceability
- 3.8 8. The Growing Importance of Local Food Systems
- 3.9 Related Searches
- 3.10 FAQs
- 3.11 Tips
- 3.12 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025

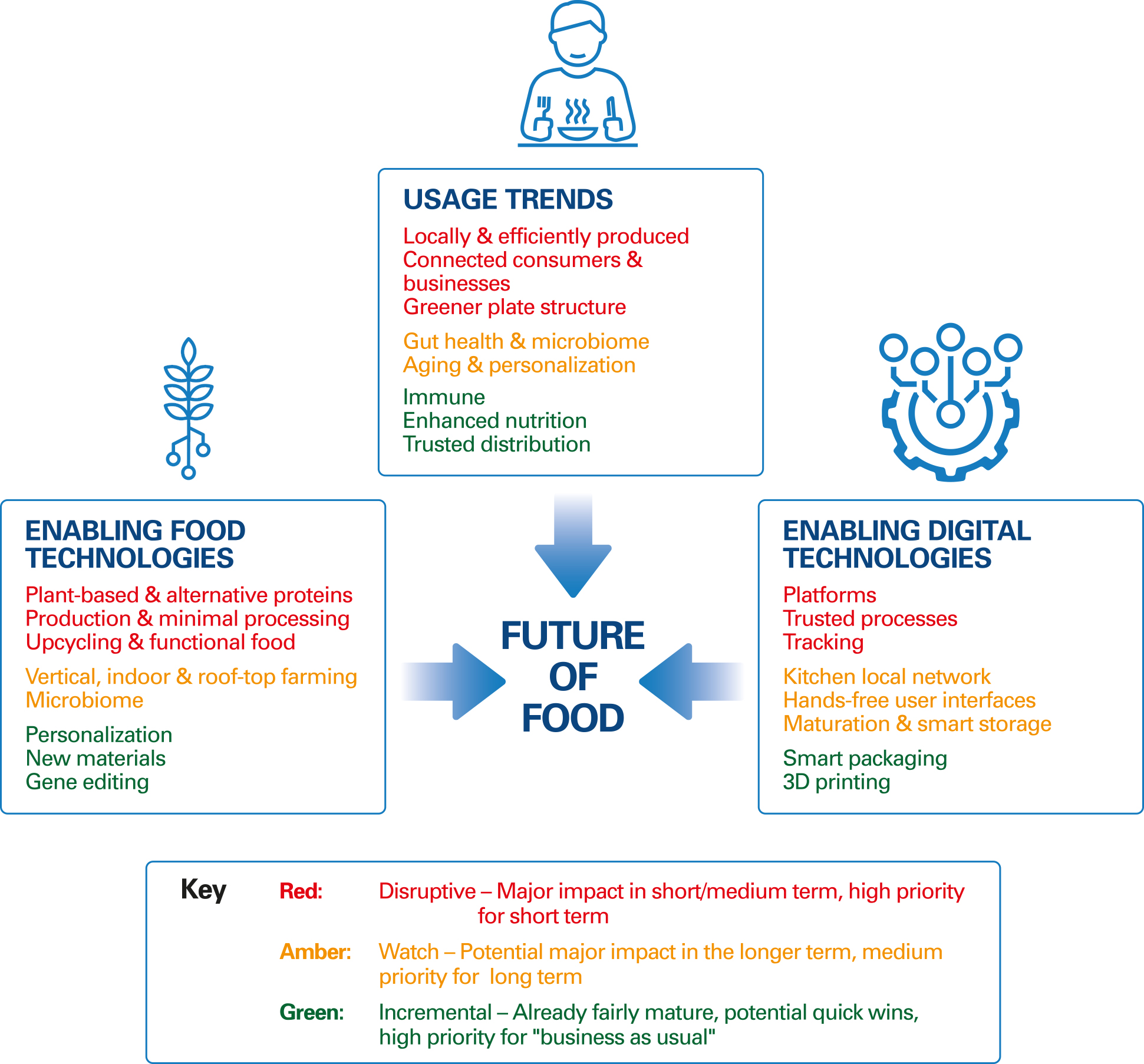
The food industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, constantly adapting to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and global challenges. As we approach 2025, several trends are poised to reshape the way food is produced, consumed, and experienced. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as it allows for informed decision-making and strategic planning in this vital sector.
Food Industry Trends 2025 are not merely predictions; they represent a confluence of factors driving innovation and change, impacting everything from farm-to-fork practices to the very definition of "food." This article will delve into eight key trends, exploring their implications and potential impact on the future of the food industry.
1. The Rise of Plant-Based Foods
The demand for plant-based alternatives continues to surge, driven by a growing awareness of environmental sustainability, animal welfare concerns, and health benefits. This trend extends beyond meat alternatives to include plant-based dairy, eggs, and even seafood.
Key Drivers:
- Environmental Sustainability: Plant-based diets have a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to animal-based diets, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and resource consumption.
- Health and Wellness: Plant-based foods are often perceived as healthier, lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, and rich in fiber and nutrients.
- Ethical Concerns: Growing numbers of consumers are concerned about animal welfare and the treatment of animals in the food industry.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in plant-based protein technology are leading to more realistic and appealing products that mimic the taste and texture of their animal-based counterparts.
Implications:
- Increased Competition: Traditional meat and dairy industries are facing increasing competition from plant-based alternatives.
- Innovation in Food Technology: Continued investment in research and development is crucial to further enhance the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of plant-based products.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: The growing acceptance of plant-based foods is changing consumer habits and preferences, creating new opportunities for innovative brands and retailers.
Examples:
- Beyond Meat: This company produces plant-based meat alternatives that have gained widespread popularity and are available in major grocery stores and restaurants.
- Impossible Foods: Similar to Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods offers plant-based burgers and other meat products that aim to replicate the taste and texture of their animal-based counterparts.
- Oatly: This brand offers a range of plant-based milk alternatives made from oats, capturing a significant share of the dairy-free market.
2. Personalized Nutrition and Dietary Needs
The era of one-size-fits-all diets is fading. Consumers are increasingly interested in personalized nutrition plans tailored to their individual needs, preferences, and health goals. This trend is fueled by advancements in genetic testing, nutritional science, and technology.
Key Drivers:
- Genetic Testing: Direct-to-consumer genetic testing kits provide insights into individual predispositions, dietary sensitivities, and optimal nutrient requirements.
- Health and Wellness Apps: Mobile applications leverage data from wearables, fitness trackers, and dietary logs to provide personalized nutrition recommendations and track progress.
- Increased Awareness of Food Sensitivities: Growing awareness of food allergies, intolerances, and sensitivities drives the demand for customized dietary solutions.
Implications:
- Personalized Food Products: The food industry is responding with tailored products and meal plans designed for specific dietary needs, such as gluten-free, dairy-free, vegan, and ketogenic options.
- Data-Driven Nutrition: Personalized nutrition plans rely heavily on data analysis and algorithms to create tailored recommendations.
- Increased Focus on Ingredient Transparency: Consumers are demanding transparency in food labeling, seeking information about ingredients, potential allergens, and nutritional content.
Examples:
- Nutrigenomics: This field studies the interaction between genes and nutrition, providing insights into personalized dietary recommendations based on individual genetic makeup.
- MyFitnessPal: This app allows users to track their food intake, exercise, and progress toward their health goals, providing personalized insights and recommendations.
- Noom: This weight-loss app combines behavioral science with personalized nutrition coaching, providing tailored guidance and support.
3. Food Waste Reduction and Sustainability
The global food system generates significant waste, contributing to environmental degradation and economic losses. Consumers are increasingly concerned about food waste and its impact on the planet, driving a demand for sustainable practices throughout the food supply chain.
Key Drivers:
- Environmental Awareness: Growing awareness of the environmental impact of food waste, including greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion, is driving consumer demand for sustainable practices.
- Economic Considerations: Reducing food waste can significantly lower costs for businesses, as it minimizes spoilage and reduces the need for excessive production.
- Government Regulations: Many countries are enacting regulations and incentives to reduce food waste, promoting responsible food management practices.
Implications:
- Innovation in Packaging: Companies are exploring innovative packaging solutions that extend shelf life and reduce spoilage, such as biodegradable materials and modified atmosphere packaging.
- Food Waste Reduction Strategies: Businesses are implementing strategies to minimize food waste, such as implementing "best before" date labeling, donating surplus food, and developing technologies for food preservation.
- Circular Economy in Food: The concept of a circular economy is being applied to the food industry, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
Examples:
- Too Good To Go: This app connects consumers with businesses that have surplus food to sell at discounted prices, preventing food waste and providing affordable meals.
- Winnow: This company provides technology solutions for food waste reduction, enabling businesses to monitor, track, and reduce food waste in their kitchens.
- Food banks and charities: Organizations like Feeding America and the Salvation Army collect and distribute surplus food to people in need, reducing waste and addressing food insecurity.
4. Food Delivery and Convenience
The rise of online food ordering and delivery services has transformed how people consume food. Consumers are increasingly seeking convenient and accessible options for meals, snacks, and groceries.
Key Drivers:
- Busy Lifestyles: Fast-paced lifestyles and time constraints are driving the demand for convenient food options.
- Technological Advancements: Mobile apps and online platforms have made ordering and delivery seamless and accessible.
- Increased Competition: The food delivery market is highly competitive, with numerous platforms vying for customer loyalty and market share.
Implications:
- Growth of Delivery Services: Food delivery platforms are expanding their reach, offering a wider selection of restaurants and cuisines.
- Integration with Online Retail: Grocery delivery services are becoming increasingly popular, blurring the lines between traditional supermarkets and online retailers.
- Focus on Convenience: Restaurants and food businesses are adapting to the convenience trend, offering online ordering, pre-prepared meals, and meal kits.
Examples:
- Uber Eats: This platform offers a wide selection of restaurants and cuisines for delivery in major cities worldwide.
- DoorDash: Similar to Uber Eats, DoorDash connects customers with local restaurants for food delivery.
- Instacart: This service provides grocery delivery from major retailers, allowing consumers to order groceries online and have them delivered to their homes.
5. The Rise of the "Conscious Consumer"
Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the social and environmental impact of their food choices. They are seeking out products that align with their values, such as ethically sourced ingredients, sustainable farming practices, and fair trade practices.
Key Drivers:
- Social Responsibility: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the social and environmental impact of their purchases.
- Transparency and Traceability: Demand for transparency in the food supply chain is growing, with consumers wanting to know the origin and production methods of their food.
- Ethical Consumption: Consumers are prioritizing brands that align with their values, such as fair labor practices, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability.
Implications:
- Increased Demand for Sustainable Products: Businesses are responding by offering certified organic, fair trade, and locally sourced products.
- Focus on Ethical Sourcing: Companies are investing in ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that their ingredients are produced in a responsible and sustainable manner.
- Transparency and Labeling: Increased emphasis on labeling and certifications that communicate the ethical and sustainable practices of food producers.
Examples:
- Fair Trade Certified: This certification ensures that products are sourced from farmers who receive fair wages and work in safe and ethical conditions.
- Organic Certification: This certification guarantees that food products are produced without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms.
- B Corp Certification: This certification recognizes companies that meet high standards of social and environmental performance, transparency, and accountability.
6. Food Technology and Innovation
The food industry is embracing technological advancements to improve efficiency, sustainability, and the consumer experience. This includes innovations in food production, processing, packaging, and distribution.
Key Drivers:
- Big Data and Analytics: Data analysis is being used to optimize food production, predict consumer demand, and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being employed for tasks such as quality control, food safety monitoring, and personalized recipe generation.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics are being used to automate tasks in food processing and packaging, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Implications:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Technology is driving improvements in food production, processing, and distribution, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Enhanced Food Safety and Quality: AI and data analytics are being used to monitor food safety, detect potential contamination, and ensure product quality.
- Personalized Food Experiences: Technology is enabling personalized food experiences, such as customized meal plans, interactive recipes, and personalized nutrition recommendations.
Examples:
- Vertical Farming: This innovative approach to agriculture uses vertical layers to grow crops in controlled environments, maximizing space and resource efficiency.
- Precision Agriculture: Using sensors and data analysis, precision agriculture optimizes farming practices, reducing waste and improving yields.
- 3D Food Printing: This technology allows for the creation of complex food structures and customized meals, offering new possibilities for food design and production.
7. Food Safety and Traceability
Consumers are increasingly concerned about food safety and the traceability of their food products. This trend is driven by concerns about foodborne illnesses, food fraud, and the desire for greater transparency in the food supply chain.
Key Drivers:
- Foodborne Illness Outbreaks: Outbreaks of foodborne illnesses highlight the importance of food safety and the need for effective food safety protocols.
- Food Fraud: Cases of food fraud, such as the adulteration of food products, have increased consumer concerns about the authenticity and safety of their food.
- Consumer Demand for Transparency: Consumers want to know where their food comes from and how it was produced, driving the demand for traceable food products.
Implications:
- Increased Food Safety Regulations: Governments are implementing stricter food safety regulations and enforcement measures to protect consumers.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is being used to track food products from farm to fork, providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of their journey.
- Data-Driven Food Safety: Data analysis and AI are being used to identify potential food safety risks and develop proactive solutions.
Examples:
- GS1 Standards: These standards provide a framework for product identification, traceability, and data exchange throughout the food supply chain.
- Walmart’s Food Safety Program: This program uses blockchain technology to track the origin and movement of produce, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- IBM Food Trust: This platform uses blockchain technology to track food products from farm to table, providing consumers with information about their origins and journey.
8. The Growing Importance of Local Food Systems
Consumers are increasingly seeking out locally sourced food, supporting their communities and reducing their environmental impact. This trend is driven by a desire for fresh, seasonal produce, a connection to their food sources, and a commitment to local economies.
Key Drivers:
- Sustainability: Local food systems reduce transportation distances, minimizing carbon emissions and supporting sustainable agriculture.
- Community Support: Buying local food helps to support local farmers and businesses, strengthening the community economy.
- Freshness and Quality: Locally sourced food is often considered fresher and higher quality, as it travels shorter distances and is less likely to be processed or preserved.
Implications:
- Growth of Farmers Markets and Local Food Retailers: Farmers markets and local food stores are becoming increasingly popular, providing consumers with access to fresh, locally grown produce.
- Community Supported Agriculture (CSA): CSAs allow consumers to subscribe to a local farm, receiving a regular supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season.
- Support for Local Agriculture: The growing demand for local food is encouraging investment in local agriculture, supporting sustainable farming practices and food security.
Examples:
- Local Harvest: This online platform connects consumers with local farmers markets, CSAs, and other food sources in their area.
- Farmers Markets: These markets provide a direct link between consumers and local farmers, offering fresh, seasonal produce.
- Community Gardens: Community gardens provide opportunities for residents to grow their own food, promoting local food production and community engagement.
Related Searches
The trends outlined above are interconnected and fuel further exploration. Here are eight related searches that offer deeper insights into the dynamic landscape of the food industry in 2025:
- Food Packaging Trends: This area explores innovative packaging materials, designs, and technologies aimed at extending shelf life, enhancing sustainability, and improving consumer convenience.
- Food Safety Technology: This field examines the role of technology in enhancing food safety, including sensor networks, AI-powered monitoring systems, and blockchain solutions for traceability.
- Future of Food Production: This topic explores emerging technologies and practices that are transforming food production, such as vertical farming, precision agriculture, and cellular agriculture.
- Food Waste Solutions: This area focuses on innovative solutions for reducing food waste, including technologies for food preservation, repurposing food waste into other products, and promoting composting.
- Food Delivery and Logistics: This topic examines the evolution of food delivery services, logistics optimization, and the impact of automation and robotics on the food supply chain.
- Consumer Trends in Food: This area explores changing consumer preferences and behaviors, including the growing demand for plant-based foods, personalized nutrition, and ethical sourcing.
- Food and Sustainability: This topic examines the role of the food industry in promoting environmental sustainability, reducing carbon footprint, and protecting natural resources.
- Food Innovation and Startups: This area explores the emergence of new food startups and innovative ideas that are disrupting the traditional food industry.
FAQs
What are the biggest challenges facing the food industry in 2025?
The food industry faces numerous challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting agricultural yields, water availability, and food security, posing significant challenges for food production and distribution.
- Food Security: Growing populations and changing dietary patterns are increasing pressure on food systems, creating challenges in ensuring food security for all.
- Sustainability: The food industry must address its environmental impact, reducing waste, promoting sustainable farming practices, and minimizing carbon emissions.
- Labor Shortages: The food industry is facing labor shortages, particularly in agriculture and food processing, which can impact production and distribution.
- Consumer Expectations: Consumers are demanding higher quality, greater transparency, and more sustainable food products, requiring businesses to adapt to changing preferences.
How can businesses prepare for the trends shaping the food industry in 2025?
Businesses can prepare for the future of food by:
- Embracing Innovation: Investing in research and development, exploring new technologies, and adopting innovative practices to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and consumer experience.
- Understanding Consumer Preferences: Staying abreast of changing consumer preferences, such as the growing demand for plant-based foods, personalized nutrition, and sustainable products.
- Building Strong Supply Chains: Ensuring robust and resilient supply chains that are adaptable to changing conditions and disruptions.
- Promoting Transparency and Traceability: Providing consumers with clear information about the origin, production methods, and ethical practices behind their food products.
- Focusing on Sustainability: Adopting sustainable practices throughout the supply chain, reducing waste, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting responsible sourcing.
What are the potential benefits of these trends for consumers?
The trends shaping the food industry in 2025 offer numerous potential benefits for consumers, including:
- Greater Access to Healthy and Sustainable Food: Increased availability of plant-based alternatives, personalized nutrition options, and sustainable food products.
- Improved Food Safety and Traceability: Enhanced food safety measures, greater transparency in the food supply chain, and access to information about the origin and production methods of their food.
- More Convenient and Accessible Food Options: Increased convenience and accessibility of food delivery services, online ordering, and grocery delivery.
- Greater Choice and Customization: A wider selection of food products, customized meal plans, and personalized nutrition recommendations.
- Support for Local Communities and Sustainable Agriculture: The opportunity to support local farmers, businesses, and sustainable agricultural practices.
Tips
Here are some practical tips for businesses and individuals navigating the food industry trends in 2025:
For Businesses:
- Invest in Technology: Embrace technological advancements to improve efficiency, enhance food safety, and personalize customer experiences.
- Focus on Sustainability: Implement sustainable practices throughout the supply chain, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact.
- Prioritize Transparency: Provide consumers with clear and accurate information about the origin, production methods, and ethical practices behind your products.
- Adapt to Changing Consumer Preferences: Stay abreast of evolving consumer demands, such as the growing demand for plant-based foods, personalized nutrition, and convenience.
- Build Strong Partnerships: Collaborate with other businesses, farmers, and organizations to create a more resilient and sustainable food system.
For Individuals:
- Make Informed Choices: Be aware of the trends shaping the food industry and make informed choices that align with your values and priorities.
- Support Local Farmers and Businesses: Buy locally sourced food whenever possible, supporting your community and promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Reduce Food Waste: Practice mindful consumption, plan meals in advance, and compost food scraps to minimize waste.
- Explore New Food Options: Try plant-based alternatives, personalized meal plans, and other innovative food products.
- Advocate for Change: Support organizations that are working to address food security, sustainability, and other challenges facing the food industry.
Conclusion
The food industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by a confluence of factors that are reshaping how food is produced, consumed, and experienced. Understanding the trends shaping the future of food is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as it enables informed decision-making and strategic planning in this vital sector. By embracing innovation, prioritizing sustainability, and adapting to changing consumer preferences, businesses can navigate the challenges and opportunities of the evolving food landscape. Consumers, in turn,







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future of Food: Trends Shaping the Industry in 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!