Shaping The Future Of Healthcare: Trends In Digital Health 2025
Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025
- 3.1 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Healthcare:
- 3.2 2. The Rise of Telehealth and Virtual Care:
- 3.3 3. Wearable Technology and Connected Healthcare:
- 3.4 4. The Rise of Personalized Medicine:
- 3.5 5. Blockchain Technology in Healthcare:
- 3.6 6. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT):
- 3.7 7. Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) in Healthcare:
- 3.8 8. The Role of Data Analytics and Big Data:
- 3.9 FAQs on Trends in Digital Health 2025
- 3.10 Tips for Healthcare Professionals and Organizations
- 3.11 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025
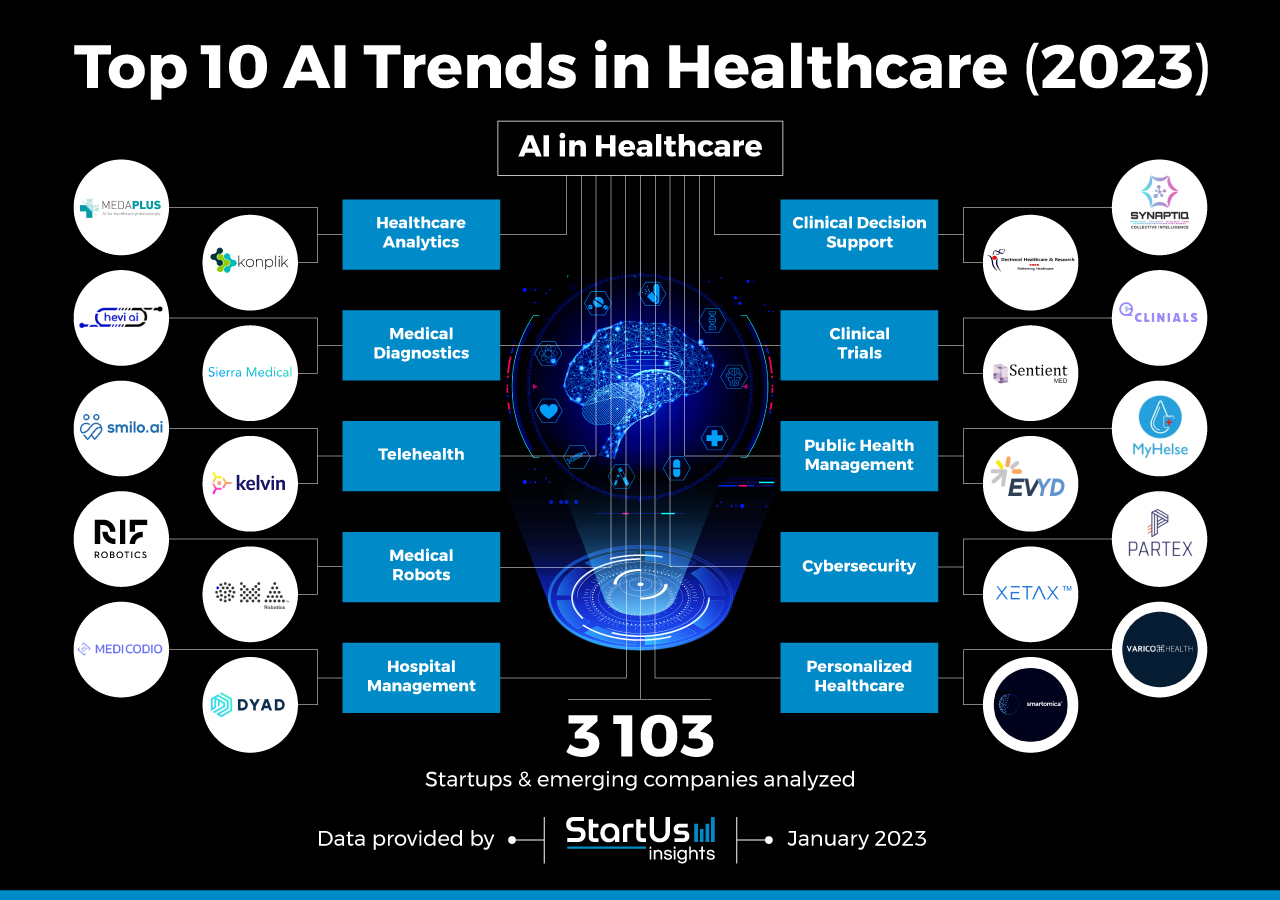
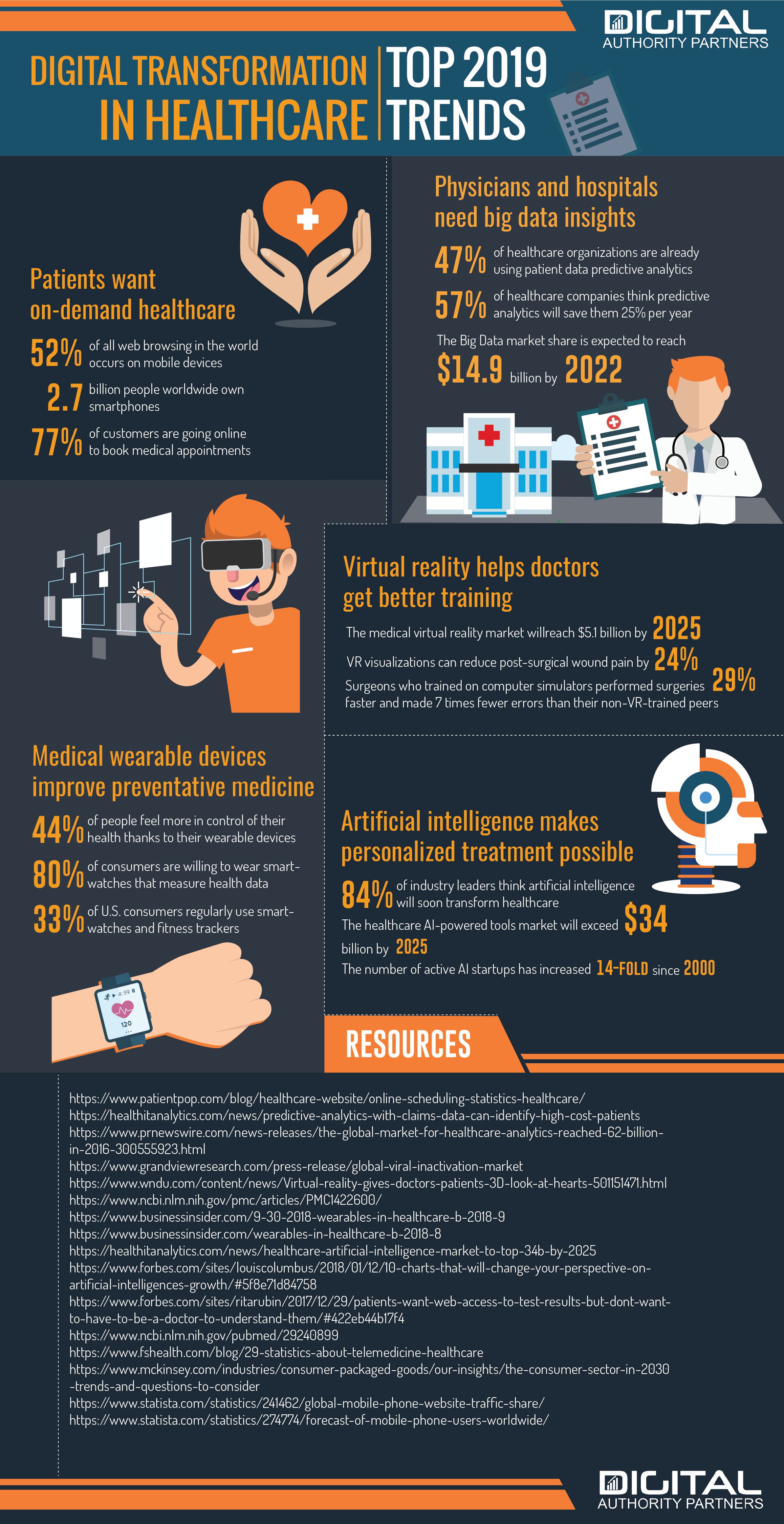
The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the relentless advancements in technology. This evolution, often referred to as digital health, is poised to revolutionize how we access, manage, and experience healthcare in the coming years. Looking ahead to 2025, several key trends are shaping the future of this dynamic field, promising a more personalized, efficient, and accessible healthcare system.
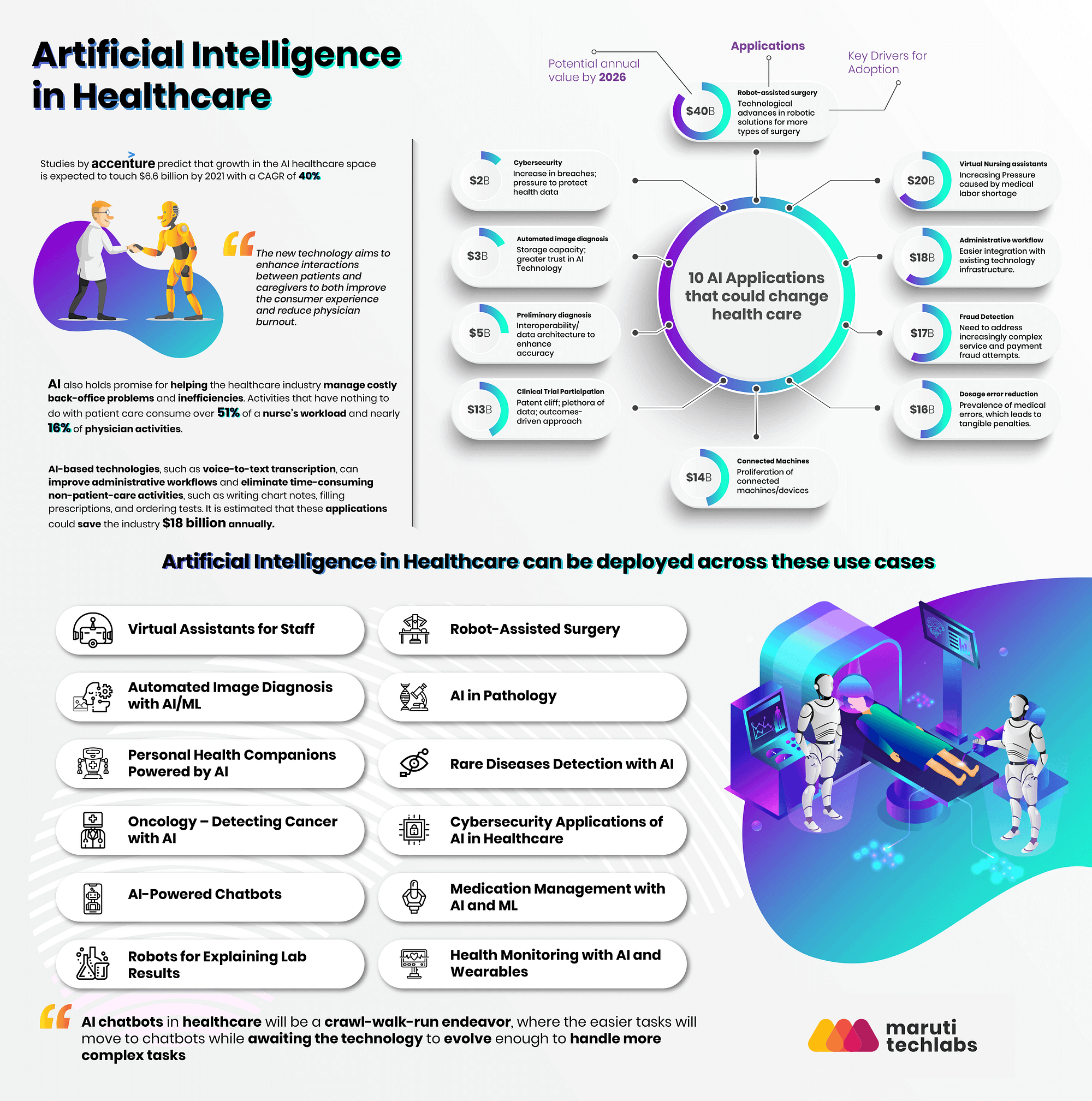
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Healthcare:
AI and ML are no longer futuristic concepts; they are becoming integral to various aspects of healthcare. From disease diagnosis and treatment planning to drug discovery and personalized medicine, these technologies are revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals work and patients receive care.
Benefits of AI and ML in Healthcare:
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze medical images, patient data, and genetic information to identify potential diseases with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By analyzing patient data and medical records, AI can tailor treatment plans to individual needs, improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI is accelerating the process of drug discovery by identifying potential drug candidates and optimizing drug development strategies.
- Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention: AI can analyze large datasets to identify risk factors for specific diseases, enabling proactive interventions and disease prevention.
- Improved Patient Engagement and Communication: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide patients with personalized health information, answer questions, and schedule appointments, improving patient engagement and communication.
Examples of AI and ML Applications in Healthcare:
- IBM Watson for Oncology: This AI system assists oncologists in developing personalized cancer treatment plans by analyzing patient data and clinical trials.
- Google’s DeepMind: This AI platform is being used to develop algorithms for early disease detection, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
- PathAI: This company uses AI to analyze pathology images, improving the accuracy and speed of cancer diagnosis.
Challenges of AI and ML in Healthcare:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is crucial when using AI and ML in healthcare.
- Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms can be biased, leading to unfair treatment outcomes. Careful consideration of data bias and algorithmic fairness is essential.
- Transparency and Explainability: It is important to understand how AI algorithms make decisions, particularly in healthcare where decisions can have significant consequences.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical questions about data ownership, informed consent, and the potential for algorithmic bias.
2. The Rise of Telehealth and Virtual Care:
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth, and this trend is set to continue. Telehealth offers patients convenient access to healthcare services, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving accessibility for those in remote areas.
Benefits of Telehealth:
- Increased Convenience and Accessibility: Telehealth eliminates the need for travel, making healthcare more accessible for patients with mobility issues, busy schedules, or those living in rural areas.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Telehealth can reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for expensive in-person visits and hospitalizations.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Telehealth allows for more frequent and convenient communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to better patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
- Remote Monitoring and Management: Telehealth enables remote monitoring of patients’ health data, allowing for early intervention and prevention of complications.
Types of Telehealth Services:
- Telemedicine: Remote consultation with a healthcare provider via video conferencing.
- Telemonitoring: Remote monitoring of patient health data, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels.
- Teleradiology: Remote interpretation of medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs.
- Telepsychiatry: Remote mental health care services.
Challenges of Telehealth:
- Access to Technology: Not all patients have access to the technology required for telehealth services.
- Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement policies for telehealth services vary across different insurance providers.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data during telehealth consultations is essential.
- Lack of Physical Examination: Some medical conditions require a physical examination, which cannot be performed remotely.
3. Wearable Technology and Connected Healthcare:
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are becoming increasingly popular. These devices collect personal health data, providing insights into individual health patterns and enabling proactive healthcare.
Benefits of Wearable Technology:
- Continuous Health Monitoring: Wearable devices can track a variety of health metrics, including heart rate, sleep patterns, activity levels, and blood pressure.
- Early Disease Detection: By analyzing data from wearable devices, healthcare providers can identify potential health problems early on, allowing for timely intervention.
- Personalized Health Insights: Wearable devices provide individuals with personalized insights into their health data, empowering them to make informed decisions about their well-being.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Wearable devices can encourage patients to take a more active role in managing their health.
Examples of Wearable Technology in Healthcare:
- Apple Watch: This smartwatch can track heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels, and can also detect falls and irregular heart rhythms.
- Fitbit: These devices track activity levels, sleep patterns, and heart rate, providing users with personalized insights into their health.
- Garmin: Garmin devices offer a range of fitness tracking features, including heart rate monitoring, GPS tracking, and sleep analysis.
Challenges of Wearable Technology:
- Data Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy and reliability of data collected by wearable devices can vary.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: The collection and storage of personal health data raise concerns about privacy and security.
- Data Overload and Interpretation: Individuals may be overwhelmed by the amount of data collected by wearable devices, and may need assistance interpreting this information.
4. The Rise of Personalized Medicine:
Personalized medicine is an approach to healthcare that takes into account an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment to tailor treatments and preventive measures. This trend is driven by advancements in genomics, AI, and data analytics.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine:
- More Effective Treatments: By understanding an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can select the most effective treatments and minimize side effects.
- Improved Prevention Strategies: Personalized medicine can identify individuals at higher risk for specific diseases, allowing for targeted preventive measures.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By optimizing treatments and preventing disease, personalized medicine can reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
Examples of Personalized Medicine Applications:
- Pharmacogenomics: This field studies how genetic variations influence drug response, enabling the development of personalized drug regimens.
- Precision Oncology: This approach uses genetic and molecular information to tailor cancer treatment plans to individual patients.
- Personalized Nutrition: Personalized nutrition plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup and lifestyle can help optimize diet and improve health outcomes.
Challenges of Personalized Medicine:
- Cost of Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can be expensive, limiting access to personalized medicine for some individuals.
- Data Privacy and Security: The collection and use of genetic data raise concerns about privacy and security.
- Ethical Considerations: There are ethical considerations related to the use of genetic information, such as potential for discrimination and genetic engineering.
5. Blockchain Technology in Healthcare:
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent data management capabilities, is finding applications in healthcare, particularly in areas like medical records, supply chain management, and clinical trials.
Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare:
- Secure and Transparent Data Management: Blockchain provides a secure and tamper-proof platform for storing and managing sensitive patient data.
- Improved Interoperability: Blockchain can facilitate interoperability between different healthcare systems, enabling seamless data sharing.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of medical supplies and pharmaceuticals, ensuring their authenticity and safety.
- Faster and More Efficient Clinical Trials: Blockchain can streamline the process of recruiting participants and managing data in clinical trials.
Examples of Blockchain Applications in Healthcare:
- Medical Records Management: Blockchain can create a secure and tamper-proof record of patient health information, allowing for easy access and sharing.
- Drug Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of pharmaceuticals from manufacturing to distribution, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
- Clinical Trial Management: Blockchain can facilitate the recruitment and management of participants in clinical trials, reducing costs and accelerating the process.
Challenges of Blockchain in Healthcare:
- Technical Complexity: Implementing blockchain technology in healthcare requires specialized technical expertise.
- Scalability and Performance: Blockchain systems need to be scalable and performant to handle the large volumes of data generated in healthcare.
- Regulation and Compliance: The use of blockchain in healthcare needs to comply with existing regulations and privacy laws.
6. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT):
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to the network of medical devices and sensors that collect and share health data, enabling continuous monitoring and remote management of patient health.
Benefits of IoMT:
- Continuous Health Monitoring: IoMT devices can collect real-time health data, providing healthcare providers with a comprehensive picture of patient health.
- Early Disease Detection: By analyzing data from IoMT devices, healthcare providers can identify potential health problems early on, allowing for timely intervention.
- Remote Patient Management: IoMT devices enable remote monitoring and management of patients’ health, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Improved Patient Engagement: IoMT devices can empower patients to take a more active role in managing their health.
Examples of IoMT Devices:
- Smart Insulin Pumps: These devices can automatically deliver insulin based on real-time blood glucose readings.
- Wearable ECG Monitors: These devices can detect irregular heart rhythms and alert healthcare providers to potential health problems.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Systems: These systems can collect data from various IoMT devices and transmit it to healthcare providers for monitoring and management.
Challenges of IoMT:
- Data Security and Privacy: The collection and transmission of sensitive health data raises concerns about security and privacy.
- Interoperability and Integration: IoMT devices need to be interoperable and seamlessly integrated with existing healthcare systems.
- Cost and Accessibility: IoMT devices can be expensive, limiting access for some patients.
7. Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) in Healthcare:
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are finding applications in healthcare, enhancing training, surgery, rehabilitation, and patient education.
Benefits of AR/VR in Healthcare:
- Improved Surgical Training and Precision: VR simulations allow surgeons to practice complex procedures in a safe and realistic environment, improving surgical skills and reducing errors.
- Enhanced Patient Education: AR and VR can create immersive and engaging experiences for patients, helping them better understand their conditions and treatment options.
- Pain Management and Rehabilitation: VR can be used to distract patients from pain during medical procedures and to enhance rehabilitation programs.
- Mental Health Treatment: VR can create immersive environments for treating phobias, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
Examples of AR/VR Applications in Healthcare:
- VR Surgical Simulation: VR simulations allow surgeons to practice complex procedures in a safe and realistic environment, improving surgical skills and reducing errors.
- AR-Assisted Surgery: AR can overlay real-time medical data onto a surgeon’s view, enhancing surgical precision and reducing complications.
- VR for Pain Management: VR can be used to distract patients from pain during medical procedures and to enhance rehabilitation programs.
Challenges of AR/VR in Healthcare:
- Cost and Accessibility: AR/VR technology can be expensive, limiting its accessibility for some healthcare providers and patients.
- User Interface and Accessibility: AR/VR systems need to be user-friendly and accessible to a wide range of users, including patients with disabilities.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AR/VR in healthcare raises ethical questions about patient privacy, data security, and the potential for manipulation.
8. The Role of Data Analytics and Big Data:
Data analytics and big data are playing a crucial role in improving healthcare outcomes and driving efficiency. By analyzing large datasets, healthcare providers can identify trends, predict outcomes, and optimize resource allocation.
Benefits of Data Analytics in Healthcare:
- Improved Disease Prevention and Management: By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can identify risk factors for specific diseases and develop targeted interventions.
- Enhanced Treatment Outcomes: Data analytics can help identify the most effective treatments for individual patients, improving treatment outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Data analytics can help healthcare providers allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that they are available when and where they are needed.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By optimizing treatments and improving efficiency, data analytics can help reduce healthcare costs.
Examples of Data Analytics Applications in Healthcare:
- Predictive Modeling: Data analytics can be used to predict the likelihood of a patient developing a specific disease or requiring hospitalization.
- Population Health Management: Data analytics can help identify trends in disease prevalence and develop targeted interventions for specific populations.
- Resource Allocation Optimization: Data analytics can help healthcare providers optimize resource allocation, ensuring that they are available when and where they are needed.
Challenges of Data Analytics in Healthcare:
- Data Quality and Integrity: The accuracy and integrity of data are essential for effective data analysis.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is crucial when using data analytics in healthcare.
- Data Interpretation and Actionability: Healthcare providers need to be able to interpret data effectively and translate insights into actionable steps.
FAQs on Trends in Digital Health 2025
Q: How will digital health impact healthcare costs in 2025?
A: Digital health technologies are expected to significantly impact healthcare costs in 2025. While some technologies, like genetic testing, may initially increase costs, the overall impact is expected to be cost-saving. This is due to factors like:
- Early disease detection and prevention: Identifying and addressing health issues early can prevent costly hospitalizations and treatments.
- Optimized treatment plans: Personalized medicine and AI-powered diagnostics can ensure patients receive the most effective treatments, reducing unnecessary procedures and hospital stays.
- Improved efficiency: Telehealth and remote monitoring can reduce the need for expensive in-person visits and hospital admissions.
- Data-driven resource allocation: Data analytics can help optimize resource allocation, preventing waste and unnecessary spending.
Q: What are the ethical considerations surrounding digital health technologies?
A: The rapid advancement of digital health technologies raises several ethical considerations:
- Data privacy and security: Ensuring the secure storage and use of sensitive patient data is crucial.
- Algorithmic bias: AI algorithms can perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair treatment outcomes.
- Informed consent: Patients must be fully informed about the use of their data and the potential risks and benefits of digital health technologies.
- Accessibility and equity: Digital health technologies should be accessible to all patients, regardless of socioeconomic status or location.
- Job displacement: The automation of certain healthcare tasks may lead to job displacement for healthcare professionals.
Q: What are the biggest challenges facing the adoption of digital health technologies?
A: While digital health technologies offer significant potential, several challenges need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
- Interoperability: Different healthcare systems and devices need to be able to communicate and share data seamlessly.
- Data security and privacy: Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive patient data.
- Regulation and compliance: Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure the safe and ethical use of digital health technologies.
- Cost and accessibility: Digital health technologies need to be affordable and accessible to all patients.
- Healthcare workforce training: Healthcare professionals need to be trained on the use and implementation of digital health technologies.
Tips for Healthcare Professionals and Organizations
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Stay informed about the latest advancements in digital health technologies and their potential applications.
- Invest in Training and Development: Ensure your healthcare workforce is trained and equipped to utilize digital health technologies effectively.
- Prioritize Data Security and Privacy: Implement robust data security measures to protect patient information.
- Foster Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborate with technology companies and other healthcare organizations to drive innovation and adoption of digital health technologies.
- Focus on Patient Engagement: Develop strategies to engage patients in their health management and empower them to use digital health technologies.
Conclusion
The trends in digital health 2025 paint a compelling picture of a future where healthcare is more personalized, accessible, and efficient. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of these technologies are immense, promising a more proactive, data-driven, and patient-centric approach to healthcare. By embracing these trends, healthcare professionals and organizations can contribute to a healthier and more equitable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trends in Digital Health 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!