Shaping The Future Of Movement: Trends In Mobility 2025
Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles
- 3.2 2. The Electrification of Transportation
- 3.3 3. The Integration of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
- 3.4 4. The Evolution of Shared Mobility
- 3.5 5. The Rise of Micro-Mobility
- 3.6 6. The Importance of Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3.7 7. The Growing Importance of Infrastructure Development
- 3.8 8. The Increasing Focus on Sustainability
- 3.9 Related Searches:
- 3.10 FAQs:
- 3.11 Tips:
- 3.12 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025

The landscape of mobility is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements, shifting societal priorities, and a growing awareness of environmental concerns. As we approach 2025, the way we move around our cities, regions, and the world is poised for a significant evolution. This article delves into the key trends in mobility 2025, exploring their implications and potential benefits for individuals, businesses, and the planet.
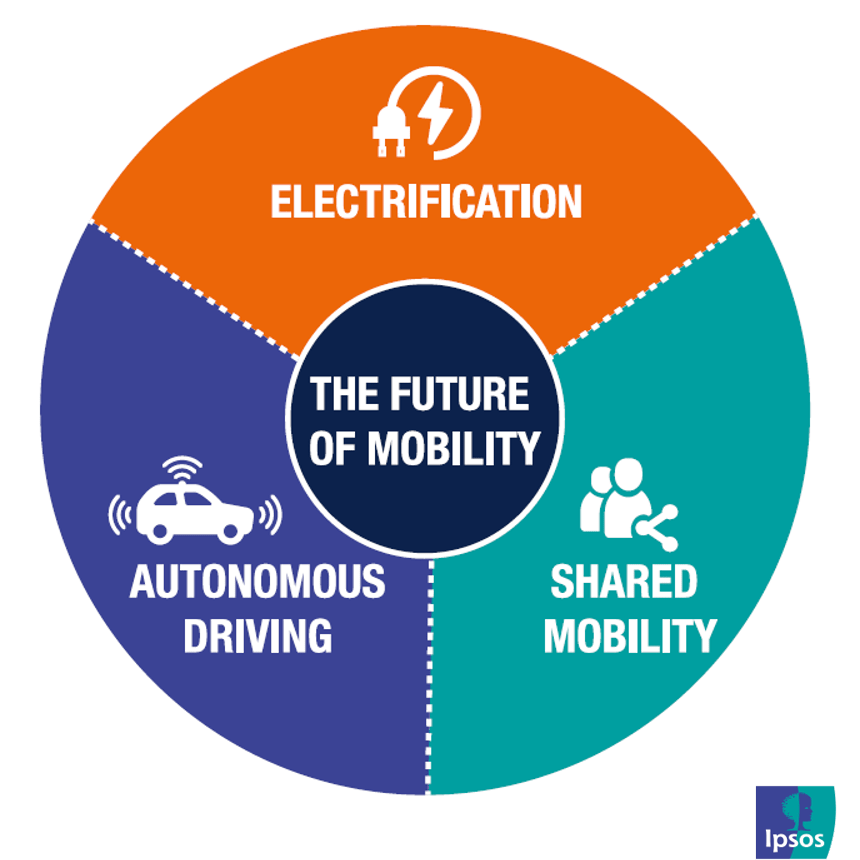
1. The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are no longer a futuristic fantasy but a rapidly developing reality. By 2025, AVs are expected to become increasingly prevalent, impacting various aspects of mobility:
- Increased Safety: AVs are programmed to adhere to traffic rules and react quickly to changing conditions, potentially reducing accidents caused by human error.
- Enhanced Accessibility: AVs can provide transportation solutions for individuals with disabilities or those who lack driving licenses, promoting greater independence and inclusivity.
- Reduced Congestion: Optimized traffic flow and efficient routing algorithms employed by AVs can significantly reduce congestion in urban areas, leading to faster commute times and improved traffic management.
- Improved Efficiency: AVs can operate 24/7, maximizing vehicle utilization and potentially lowering overall transportation costs.
The development of robust infrastructure, comprehensive regulations, and public acceptance are crucial for the widespread adoption of AVs. However, the potential impact on employment in the transportation sector and the ethical considerations surrounding decision-making algorithms require careful consideration.
2. The Electrification of Transportation
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, driven by environmental concerns and government incentives. By 2025, EVs are projected to become a significant portion of the global automotive market, with implications for:
- Reduced Emissions: EVs emit zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air quality and mitigating climate change.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs are more energy-efficient than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Lower Operating Costs: EVs typically have lower maintenance costs and benefit from lower fuel prices compared to traditional vehicles.
- Increased Infrastructure: The expansion of charging infrastructure is crucial to support the growing number of EVs on the roads, requiring investments in public charging stations and home charging solutions.
The availability of affordable EVs with longer ranges and improved battery technology will play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to electric mobility.
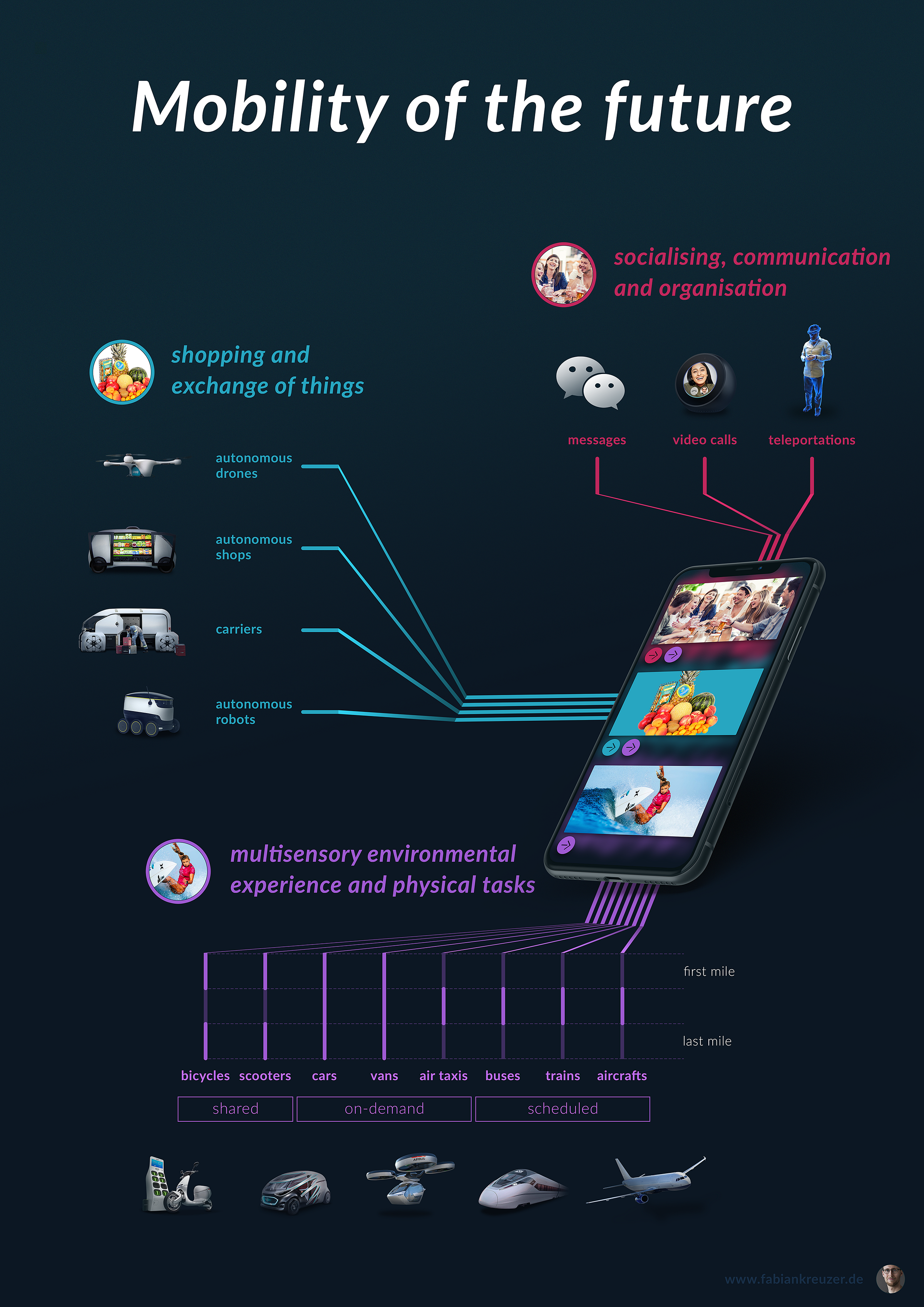
3. The Integration of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
MaaS platforms are transforming the way people access transportation by offering integrated and personalized mobility solutions. By 2025, MaaS is expected to become more prevalent, offering:
- Seamless Travel Experiences: MaaS platforms provide a single interface to plan, book, and pay for various modes of transportation, including public transit, ride-hailing, bike-sharing, and even walking or cycling.
- Increased Convenience: Users can access real-time information on service availability, estimated travel times, and potential disruptions, simplifying their journey planning.
- Reduced Travel Costs: MaaS platforms can offer bundled travel packages and dynamic pricing, potentially leading to cost savings for users.
- Improved Sustainability: By promoting the use of public transport and alternative modes of transportation, MaaS platforms can contribute to reducing traffic congestion and emissions.
The success of MaaS platforms hinges on the collaboration of various transportation providers and the development of user-friendly interfaces that cater to diverse needs and preferences.
4. The Evolution of Shared Mobility
Shared mobility options, such as ride-hailing, car-sharing, and bike-sharing, have gained immense popularity in recent years. By 2025, these services are expected to continue evolving, driven by:
- Increased Demand: The growing urban population and the preference for flexible and convenient transportation options are driving the demand for shared mobility services.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements in ride-hailing platforms, electric scooters, and self-driving technology are further enhancing the efficiency and convenience of shared mobility.
- Focus on Sustainability: Shared mobility services can contribute to reducing car ownership and promoting sustainable transportation choices.
- Integration with MaaS: Shared mobility services are increasingly being integrated into MaaS platforms, offering seamless access to a wider range of transportation options.
The integration of shared mobility with other transportation modes, such as public transit, is crucial for creating efficient and sustainable mobility ecosystems.
5. The Rise of Micro-Mobility
Micro-mobility options, including e-scooters, e-bikes, and electric skateboards, are gaining popularity as convenient and eco-friendly alternatives for short-distance trips. By 2025, micro-mobility is expected to become a significant part of urban transportation, offering:
- Last-Mile Solutions: Micro-mobility provides efficient solutions for connecting users to public transit stations or their final destinations.
- Reduced Congestion: By providing an alternative to car travel for short distances, micro-mobility can help alleviate traffic congestion in urban areas.
- Environmental Benefits: Micro-mobility options are generally electric-powered, contributing to cleaner air quality and reducing carbon emissions.
- Increased Accessibility: Micro-mobility can provide accessible and affordable transportation options for individuals who may not have access to cars or public transit.
The development of safe and regulated micro-mobility infrastructure, including designated bike lanes and parking areas, is crucial for ensuring the safety and accessibility of these services.
6. The Importance of Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Data analytics and AI are playing an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of mobility. By 2025, these technologies will be used to:
- Optimize Traffic Flow: AI algorithms can analyze real-time traffic data to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve travel times.
- Personalize Transportation Experiences: AI can learn individual travel preferences and habits to personalize transportation options, providing tailored recommendations and seamless travel experiences.
- Improve Safety: AI can analyze data from sensors and cameras to detect potential hazards, alert drivers to potential dangers, and even intervene to prevent accidents.
- Enhance Sustainability: AI can help optimize transportation routes, reduce fuel consumption, and promote the use of public transportation, contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
The ethical implications of using AI in transportation, including privacy concerns and the potential for bias in algorithms, require careful consideration and robust safeguards.
7. The Growing Importance of Infrastructure Development
The development of robust and integrated infrastructure is crucial for supporting the growth of various mobility trends. By 2025, investments in the following areas will be essential:
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: The widespread adoption of EVs necessitates the expansion of public charging stations, including fast-charging networks and home charging solutions.
- Autonomous Vehicle Infrastructure: The deployment of AVs requires the development of dedicated lanes, sensors, and communication systems to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Public Transit Improvements: Investments in public transit systems, including expanding rail networks, improving bus routes, and enhancing accessibility, are crucial for promoting sustainable mobility.
- Micro-Mobility Infrastructure: Dedicated bike lanes, parking areas, and designated micro-mobility zones are essential for ensuring the safety and accessibility of e-scooters, e-bikes, and other micro-mobility options.
The development of interconnected and multimodal transportation networks is key to creating seamless and efficient mobility ecosystems.
8. The Increasing Focus on Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important consideration in the mobility sector. By 2025, the focus on sustainable transportation will manifest in:
- Reduced Emissions: The transition to electric vehicles, the promotion of public transport, and the use of micro-mobility options will contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Shared mobility services and MaaS platforms can reduce car ownership and promote efficient vehicle utilization, minimizing resource consumption.
- Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Investments in green infrastructure, such as bike lanes, pedestrian walkways, and green spaces, can promote active transportation and create more sustainable urban environments.
- Circular Economy Principles: The adoption of circular economy principles in the transportation sector can reduce waste, promote resource efficiency, and ensure the responsible disposal of end-of-life vehicles.
The integration of sustainability considerations into all aspects of mobility planning and development is essential for building a more environmentally friendly and resilient transportation system.
Related Searches:
1. Future of Transportation: This search explores the broader vision of how transportation will evolve in the coming years, encompassing trends beyond those listed above. It delves into emerging technologies, such as hyperloop and flying cars, and their potential impact on the future of mobility.
2. Smart Cities and Mobility: This search focuses on the role of technology in shaping urban mobility. It examines how smart city initiatives, including connected infrastructure, data analytics, and AI, can optimize transportation systems and improve the quality of life for residents.
3. Mobility as a Service (MaaS) Trends: This search delves deeper into the evolution of MaaS platforms, exploring specific examples, key challenges, and future potential. It analyzes the impact of MaaS on different stakeholder groups, including individuals, businesses, and governments.
4. Autonomous Vehicle Regulations: This search examines the legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. It explores the challenges of establishing clear guidelines, ensuring safety, and addressing ethical concerns.
5. Electric Vehicle Market Outlook: This search provides a comprehensive overview of the global EV market, including sales projections, key players, and factors influencing growth. It analyzes the role of government incentives, technological advancements, and consumer adoption in driving the EV market.
6. Shared Mobility Business Models: This search explores the various business models employed by shared mobility companies, including ride-hailing, car-sharing, and bike-sharing. It analyzes the profitability, scalability, and challenges associated with different models.
7. Micro-Mobility Safety and Regulation: This search examines the safety concerns surrounding micro-mobility options, such as e-scooters and e-bikes. It explores the role of regulations, infrastructure development, and public awareness in mitigating risks and promoting safe use.
8. Sustainable Transportation Solutions: This search explores the broader landscape of sustainable transportation, encompassing various approaches to reduce environmental impact. It examines the role of public transport, cycling, walking, and alternative fuels in creating a more sustainable mobility system.
FAQs:
1. What are the biggest challenges to achieving these mobility trends by 2025?
The implementation of these trends faces several challenges:
- Infrastructure Development: Significant investments are needed to build the necessary infrastructure for EVs, AVs, and other emerging mobility solutions.
- Regulation and Policy: Clear regulations and policies are needed to govern the use of new technologies, ensuring safety, accessibility, and ethical considerations.
- Public Acceptance: Gaining public trust and acceptance for new technologies, particularly AVs, requires addressing concerns about safety, job displacement, and privacy.
- Cost and Affordability: The cost of adopting new technologies, such as EVs and AVs, needs to be made affordable for a wider range of consumers.
2. How will these trends impact urban planning and development?
The adoption of these trends will necessitate a shift in urban planning and development:
- Prioritizing Public Transport and Active Transportation: Cities will need to prioritize public transport, cycling, and walking infrastructure to reduce reliance on private vehicles.
- Designing for Autonomous Vehicles: Urban planning needs to consider the specific requirements of AVs, such as dedicated lanes and charging infrastructure.
- Creating More Walkable and Livable Cities: Cities need to prioritize pedestrian-friendly environments, green spaces, and mixed-use development to enhance the quality of life for residents.
- Addressing Social Equity: Planning needs to ensure that new mobility solutions are accessible and affordable for all residents, regardless of their income or mobility needs.
3. How can governments and businesses promote these mobility trends?
Governments and businesses can play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of these trends:
- Government Incentives: Governments can offer incentives, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and charging infrastructure development, to encourage the adoption of EVs and other sustainable mobility solutions.
- Regulation and Standards: Governments need to establish clear regulations and standards for AVs, micro-mobility, and other emerging technologies to ensure safety and public acceptance.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments and businesses is essential to develop and implement innovative mobility solutions.
- Investing in Research and Development: Governments and businesses need to invest in research and development to drive technological advancements and overcome challenges in the mobility sector.
Tips:
1. Embrace Sustainable Transportation Choices: Consider using public transport, cycling, walking, or micro-mobility options for short trips to reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable transportation system.
2. Stay Informed About Emerging Technologies: Keep abreast of the latest developments in autonomous vehicles, electric vehicles, and other emerging mobility technologies to understand their potential impact on your life and transportation choices.
3. Support Businesses Promoting Sustainable Mobility: Choose businesses that are committed to sustainable transportation practices, such as offering EV charging stations, promoting carpooling, or investing in public transport.
4. Advocate for Sustainable Mobility Policies: Engage with your local government and policymakers to advocate for policies that promote sustainable transportation, including investments in public transport, bike lanes, and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure.
Conclusion:
The future of mobility is characterized by innovation, sustainability, and a focus on enhancing the quality of life for individuals and communities. The trends discussed in this article highlight the transformative potential of emerging technologies, shifting consumer preferences, and a growing awareness of environmental concerns. By embracing these trends, we can create a more efficient, sustainable, and inclusive transportation system that meets the needs of a rapidly evolving world. The journey towards a better future of mobility is underway, and it is through collaborative efforts, technological advancements, and a commitment to sustainability that we can shape a future where movement is seamless, efficient, and environmentally responsible.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future of Movement: Trends in Mobility 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!