Technology Trends Shaping The Future: A Look At 2025 And Beyond
Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond
Related Articles: Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond
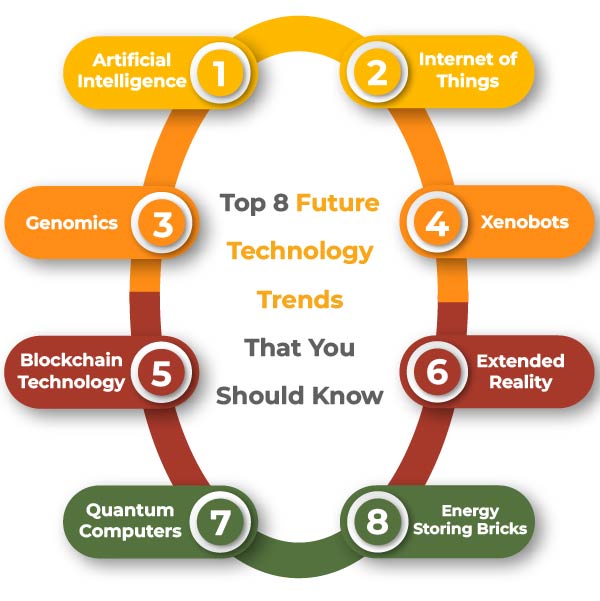
- 3.1 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): The Rise of Intelligent Automation
- 3.2 2. Extended Reality (XR): Blending Physical and Digital Worlds
- 3.3 3. Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting the Physical World
- 3.4 4. Cloud Computing: The Power of On-Demand Resources
- 3.5 5. Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing Trust and Transparency
- 3.6 6. Quantum Computing: Unlocking New Possibilities
- 3.7 7. Biotechnology and Genomics: Advancing Healthcare and Sustainability
- 3.8 8. Edge Computing: Bringing Computing Power Closer to the Source
- 3.9 FAQs about Technology Trends for the Future
- 3.10 Tips for Staying Ahead of the Curve
- 3.11 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond

The relentless march of technology continues, reshaping our world at an unprecedented pace. While predicting the future with absolute certainty is impossible, analyzing current trends and emerging technologies allows us to glimpse the landscape of 2025 and beyond. This exploration delves into eight pivotal trends, examining their potential impact on various aspects of our lives.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): The Rise of Intelligent Automation
AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s rapidly becoming a reality. From self-driving cars to personalized healthcare, AI is permeating every facet of our existence. Its ability to learn, adapt, and perform complex tasks autonomously is revolutionizing industries.
Impact:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI-powered automation streamlines processes, reducing manual labor and boosting productivity across sectors.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI analyzes vast datasets to provide data-driven insights, enabling better decision-making in business, healthcare, and government.
- Personalized Experiences: AI tailors experiences to individual needs, creating personalized recommendations, content, and services.
- New Job Opportunities: While AI may automate certain tasks, it also creates new roles in AI development, data science, and AI ethics.
Examples:
- AI in Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostic tools assist doctors in detecting diseases earlier and more accurately.
- AI in Finance: AI algorithms analyze financial data to identify fraud and predict market trends.
- AI in Customer Service: Chatbots powered by AI provide instant customer support, resolving queries and automating tasks.
2. Extended Reality (XR): Blending Physical and Digital Worlds
XR encompasses technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
Impact:
- Immersive Experiences: XR creates immersive experiences, transforming entertainment, education, and training.
- Enhanced Productivity: XR tools enhance collaboration and productivity by providing virtual workspaces and interactive training simulations.
- Improved Design and Prototyping: XR enables designers and engineers to visualize and interact with prototypes in a virtual environment.
- New Retail and Marketing Opportunities: XR allows brands to create interactive experiences, enhancing customer engagement and driving sales.
Examples:
- VR in Gaming: VR headsets offer immersive gaming experiences, transporting players into virtual worlds.
- AR in Retail: AR apps allow customers to visualize products in their own space, enhancing the shopping experience.
- MR in Training: MR simulations provide realistic training scenarios, improving skills and safety in industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
3. Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting the Physical World
The IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices, sensors, and software that collect and exchange data. This interconnectedness fuels innovation across industries.
Impact:
- Smart Homes and Cities: IoT enables smart homes with automated systems and connected appliances, while smart cities leverage data for improved traffic management, resource optimization, and public safety.
- Industrial Automation: IoT sensors monitor and control industrial processes, enhancing efficiency, reducing downtime, and optimizing production.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Wearable devices and connected medical devices provide real-time health data, enabling personalized healthcare and remote patient monitoring.
- Enhanced Security: IoT devices equipped with sensors and cameras improve security measures, detecting threats and providing real-time alerts.
Examples:
- Smart Home Appliances: Connected refrigerators track inventory, while smart thermostats optimize energy consumption.
- Connected Cars: Vehicles equipped with sensors and connectivity features enhance safety, navigation, and fuel efficiency.
- Industrial Automation: IoT sensors monitor machine performance, predict failures, and optimize production processes.
4. Cloud Computing: The Power of On-Demand Resources
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources like servers, storage, and software over the internet. It eliminates the need for expensive hardware investments, enabling scalability and flexibility.
Impact:
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing reduces hardware costs, lowers IT maintenance expenses, and allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
- Increased Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration, enabling teams to work together remotely on shared documents and projects.
- Improved Data Security: Cloud providers offer robust security measures, safeguarding data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Examples:
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox provide secure and accessible storage for files and documents.
- Cloud Computing Platforms: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer a wide range of cloud services for businesses.
- Cloud-Based Software: Applications like Salesforce and Slack are hosted on cloud servers, accessible from any device with internet access.
5. Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing Trust and Transparency
Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable ledger that records transactions securely and transparently. It has the potential to revolutionize various sectors by fostering trust and efficiency.
Impact:
- Secure Transactions: Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing fraud and increasing transaction security.
- Increased Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and auditable trail.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Blockchain tracks products throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and provenance.
- New Business Models: Blockchain enables new business models, like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Examples:
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular cryptocurrencies built on blockchain technology.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain tracks the origin and movement of goods, ensuring product authenticity and safety.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain can secure and manage digital identities, reducing fraud and identity theft.
6. Quantum Computing: Unlocking New Possibilities
Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems that are impossible for classical computers. Its potential applications are vast and transformative.
Impact:
- Drug Discovery and Materials Science: Quantum computers can accelerate drug discovery and materials research by simulating complex molecular interactions.
- Financial Modeling and Optimization: Quantum algorithms can optimize financial portfolios and analyze market trends with unprecedented accuracy.
- Artificial Intelligence: Quantum computing can enhance AI algorithms, enabling faster learning and more efficient data processing.
- Cybersecurity: Quantum cryptography can create unbreakable encryption methods, safeguarding sensitive data from cyberattacks.
Examples:
- Drug Discovery: Quantum computers can simulate the behavior of molecules, accelerating the development of new drugs and therapies.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum algorithms can optimize investment strategies and predict market trends with greater accuracy.
- Materials Science: Quantum computers can design new materials with enhanced properties for various applications.
7. Biotechnology and Genomics: Advancing Healthcare and Sustainability
Biotechnology and genomics are transforming healthcare and other industries by leveraging the power of biological processes and genetic information.
Impact:
- Personalized Medicine: Genomics allows for personalized treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup, leading to more effective therapies and reduced side effects.
- Disease Prevention and Early Detection: Genetic testing can identify individuals at risk for certain diseases, enabling early intervention and preventive measures.
- Bioengineered Products: Biotechnology creates bioengineered products like biofuels and bioplastics, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Agricultural Innovation: Genomics enhances crop yields and disease resistance, improving food security and sustainability.
Examples:
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy aims to correct genetic defects by replacing faulty genes with healthy ones, offering treatment for inherited diseases.
- Precision Medicine: Personalized medicine uses genetic information to tailor treatments for individual patients.
- Biofuels: Biotechnology produces biofuels from renewable sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
8. Edge Computing: Bringing Computing Power Closer to the Source
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. It is essential for real-time applications and data-intensive tasks.
Impact:
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel between devices and data centers, improving performance for applications requiring real-time data processing.
- Enhanced Security: Processing data locally reduces the risk of data breaches and improves security for sensitive information.
- Improved Scalability and Reliability: Edge computing distributes processing power, enhancing scalability and reliability, especially for geographically dispersed networks.
- New Applications: Edge computing enables new applications like autonomous vehicles, smart factories, and remote healthcare monitoring.
Examples:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing processes data from sensors in real-time, enabling self-driving cars to navigate safely and efficiently.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing monitors and controls industrial processes, optimizing production and reducing downtime.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing enables real-time traffic management, resource optimization, and public safety measures.
FAQs about Technology Trends for the Future
1. What are the biggest challenges facing the adoption of these technologies?
- Ethical Concerns: AI, blockchain, and biotechnology raise ethical concerns regarding privacy, bias, and the potential for misuse.
- Security Risks: The interconnected nature of IoT and cloud computing increases vulnerability to cyberattacks.
- Skills Gap: The rapid evolution of technology requires a skilled workforce, creating a gap between the demand for tech professionals and the available talent.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Implementing these technologies requires significant infrastructure investments, which can be a barrier for some businesses.
2. How will these trends impact the job market?
- Automation of Tasks: AI and automation will automate many routine tasks, potentially displacing some jobs.
- New Job Opportunities: However, these technologies will also create new roles in areas like AI development, data science, cybersecurity, and XR design.
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Workers will need to adapt and acquire new skills to thrive in a technology-driven economy.
3. What are the potential benefits of these technologies for society?
- Improved Healthcare: AI, genomics, and biotechnology offer the potential for personalized medicine, early disease detection, and new treatments.
- Enhanced Sustainability: IoT, blockchain, and biotechnology contribute to sustainable practices, reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and developing renewable energy sources.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency: AI, XR, and cloud computing enhance productivity and efficiency across industries.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: AI, IoT, and blockchain contribute to improved safety and security in areas like transportation, healthcare, and cybersecurity.
4. What are the risks associated with these technologies?
- Job Displacement: Automation could lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Data Privacy and Security: The collection and use of personal data raise concerns about privacy and security breaches.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can perpetuate existing biases if trained on biased data.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI, biotechnology, and other advanced technologies raises ethical questions about human autonomy, responsibility, and the potential for misuse.
Tips for Staying Ahead of the Curve
- Continuously Learn and Adapt: Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends by reading industry publications, attending conferences, and engaging in online learning platforms.
- Embrace Experimentation: Encourage experimentation and exploration of new technologies within your organization.
- Develop a Future-Proof Workforce: Invest in training and development programs to equip your employees with the skills needed for the future of work.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Create an environment that encourages creativity, collaboration, and the pursuit of new ideas.
Conclusion
Technology is a powerful force shaping our world, and its influence will continue to grow in the years to come. Understanding the trends discussed above is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. By embracing these technologies, we can unlock new opportunities, address global challenges, and create a brighter future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Technology Trends Shaping the Future: A Look at 2025 and Beyond. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!