Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Foundation: Periodic Trends
- 3.2 Key Periodic Trends Explored in Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
- 3.3 Benefits of Using Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
- 3.4 FAQs About Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
- 3.5 Tips for Using Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements based on their atomic structure and resulting properties. Activity periodic trends – webquest answer key 2025 is a resource designed to help students explore and understand these trends, providing a framework for analyzing and predicting the behavior of elements. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key concepts, benefits, and practical applications of this resource.
The Foundation: Periodic Trends
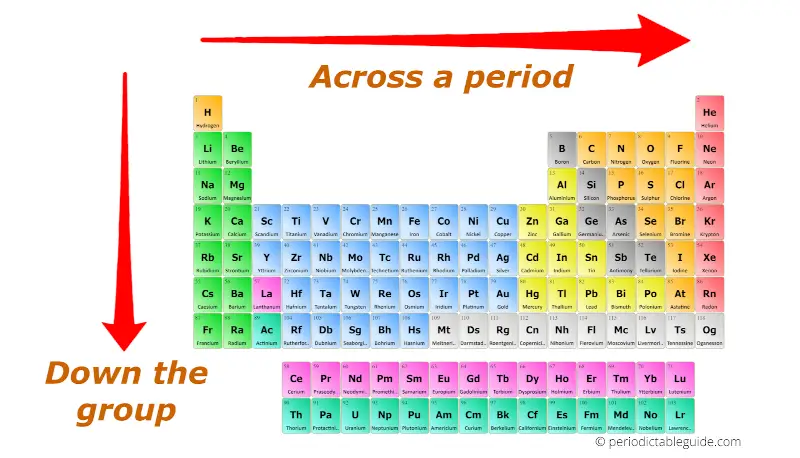
Periodic trends are predictable patterns in the chemical properties of elements as you move across periods (horizontal rows) and down groups (vertical columns) of the periodic table. Understanding these trends allows us to:
- Predict the reactivity of elements: Knowing where an element sits on the periodic table can tell us how likely it is to form bonds with other elements, participate in chemical reactions, and exhibit specific properties.
- Explain the behavior of elements: Periodic trends provide a framework for understanding the underlying reasons behind the observed chemical and physical properties of elements.
- Design and synthesize new materials: By leveraging our understanding of periodic trends, scientists can design new materials with specific properties for various applications.
Key Periodic Trends Explored in Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025 focuses on key periodic trends, including:
1. Atomic Radius: The size of an atom, measured as the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Atomic radius generally:
- Decreases across a period: As you move across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, attracting the electrons more strongly and pulling them closer to the nucleus.
- Increases down a group: Moving down a group, additional electron shells are added, increasing the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
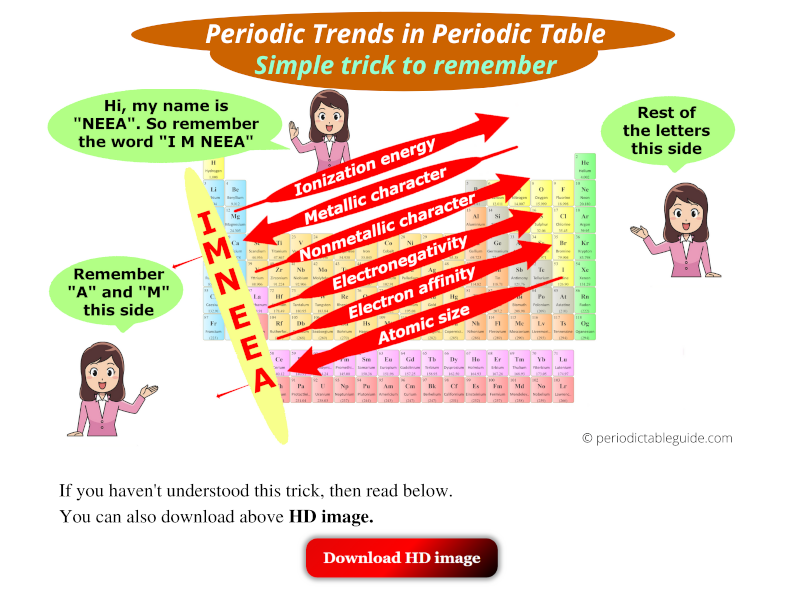
2. Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Ionization energy generally:
- Increases across a period: Electrons are more strongly attracted to the nucleus across a period, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
- Decreases down a group: Electrons in outer shells are further from the nucleus and experience weaker attraction, making them easier to remove.
3. Electron Affinity: The change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state. Electron affinity generally:
- Increases across a period: Atoms with a stronger attraction to electrons have a greater tendency to gain electrons, resulting in a more negative electron affinity.
- Decreases down a group: Electrons are added to higher energy levels, experiencing weaker attraction to the nucleus, leading to a less negative or even positive electron affinity.
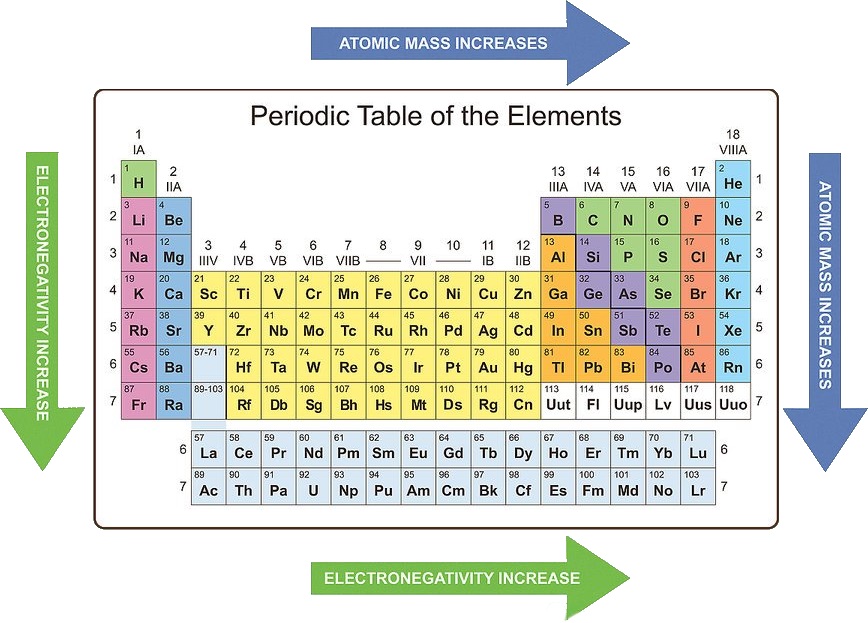
4. Electronegativity: The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons towards itself. Electronegativity generally:
- Increases across a period: Atoms with a stronger attraction to electrons have a higher electronegativity.
- Decreases down a group: Electrons are further from the nucleus, experiencing weaker attraction, leading to lower electronegativity.
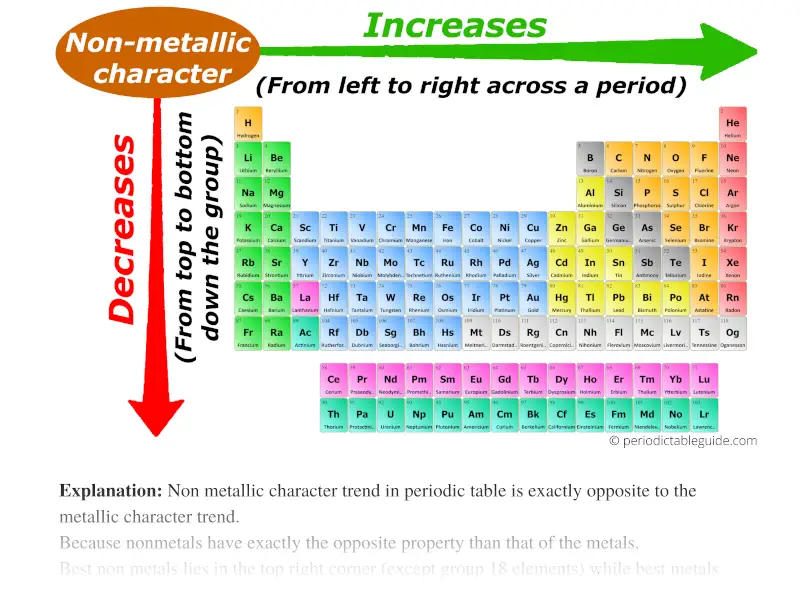
5. Metallic Character: The tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions (cations). Metallic character generally:
- Decreases across a period: Electrons are more tightly held by the nucleus, making it less likely to lose electrons and form cations.
- Increases down a group: Electrons are further from the nucleus, making it easier to lose electrons and form cations.
6. Reactivity: The tendency of an element to participate in chemical reactions. Reactivity is influenced by various factors, including ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
- Metals: Metals generally have low ionization energies, making them highly reactive, especially in the presence of nonmetals.
- Nonmetals: Nonmetals typically have high ionization energies and electron affinities, making them reactive with metals and other nonmetals.
7. Oxidation States: The charge an atom has when it forms an ion. Oxidation states are related to the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell) and the element’s position on the periodic table.
- Metals: Metals tend to have positive oxidation states, losing electrons to form cations.
- Nonmetals: Nonmetals tend to have negative oxidation states, gaining electrons to form anions.
8. Physical Properties: Periodic trends also influence physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density.
- Metals: Metals generally have high melting and boiling points due to strong metallic bonds.
- Nonmetals: Nonmetals exhibit a wider range of physical properties, with some being solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature.
Benefits of Using Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025 offers several benefits for students:
- Interactive Learning: The webquest format provides an engaging and interactive learning experience, encouraging students to actively explore and discover periodic trends.
- Hands-on Exploration: Students engage with real-world examples and applications of periodic trends, making the learning process more concrete and relatable.
- Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: The webquest challenges students to analyze data, draw conclusions, and solve problems related to periodic trends, fostering critical thinking skills.
- Self-Directed Learning: The webquest encourages self-directed learning, allowing students to work at their own pace and explore topics in more depth.
- Collaboration and Communication: The webquest can be used in collaborative settings, fostering communication and teamwork skills among students.
FAQs About Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
Q: What is the target audience for Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025?
A: This resource is designed for students studying chemistry at the high school or introductory college level. It provides a foundation for understanding periodic trends and their applications.
Q: What specific skills does Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025 help students develop?
A: This resource helps students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication skills. It also encourages self-directed learning and fosters an understanding of scientific concepts.
Q: How can teachers incorporate Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025 into their curriculum?
A: Teachers can use this webquest as a supplement to their existing curriculum, providing students with an interactive and engaging way to learn about periodic trends. It can also be used as a stand-alone activity for independent study or group projects.
Q: What are some examples of real-world applications of periodic trends?
A: Understanding periodic trends has applications in various fields, including:
- Materials science: Designing new materials with specific properties, like conductivity, strength, or reactivity.
- Medicine: Developing new drugs and treatments based on the properties of elements.
- Environmental science: Understanding the environmental impact of different elements and their compounds.
- Energy production: Developing new energy technologies based on the properties of elements.
Tips for Using Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025
- Prioritize understanding: Encourage students to focus on understanding the concepts behind periodic trends rather than simply memorizing facts.
- Use real-world examples: Integrate real-world examples and applications of periodic trends to make the learning process more relevant and engaging.
- Encourage collaboration: Facilitate collaborative learning by allowing students to work in groups and share their findings.
- Provide feedback and support: Provide regular feedback and support to students as they work through the webquest, ensuring they understand the concepts and are on track.
Conclusion
Activity Periodic Trends – Webquest Answer Key 2025 provides a valuable resource for students to explore and understand the fundamental concepts of periodic trends. By engaging with interactive activities, exploring real-world applications, and developing critical thinking skills, students can gain a deeper understanding of the periodic table and its significance in chemistry and beyond. This resource can be a valuable tool for educators and students alike, fostering a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of chemistry and the interconnectedness of elements.
.PNG)
/periodictrendstable-5c4a46614cedfd000187c5db.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!